Digitalization and the Anthropocene
*1. Handwritten notes

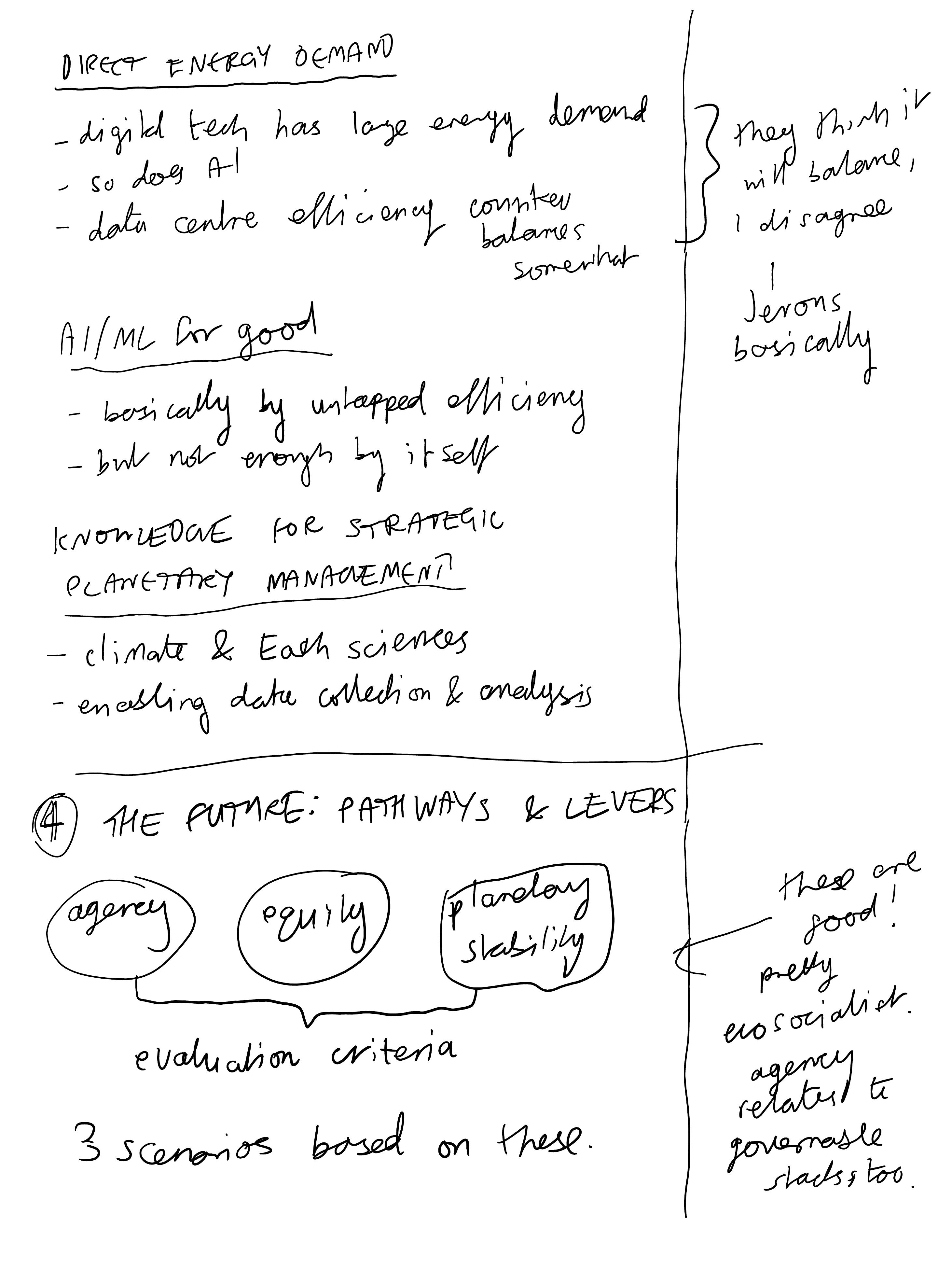
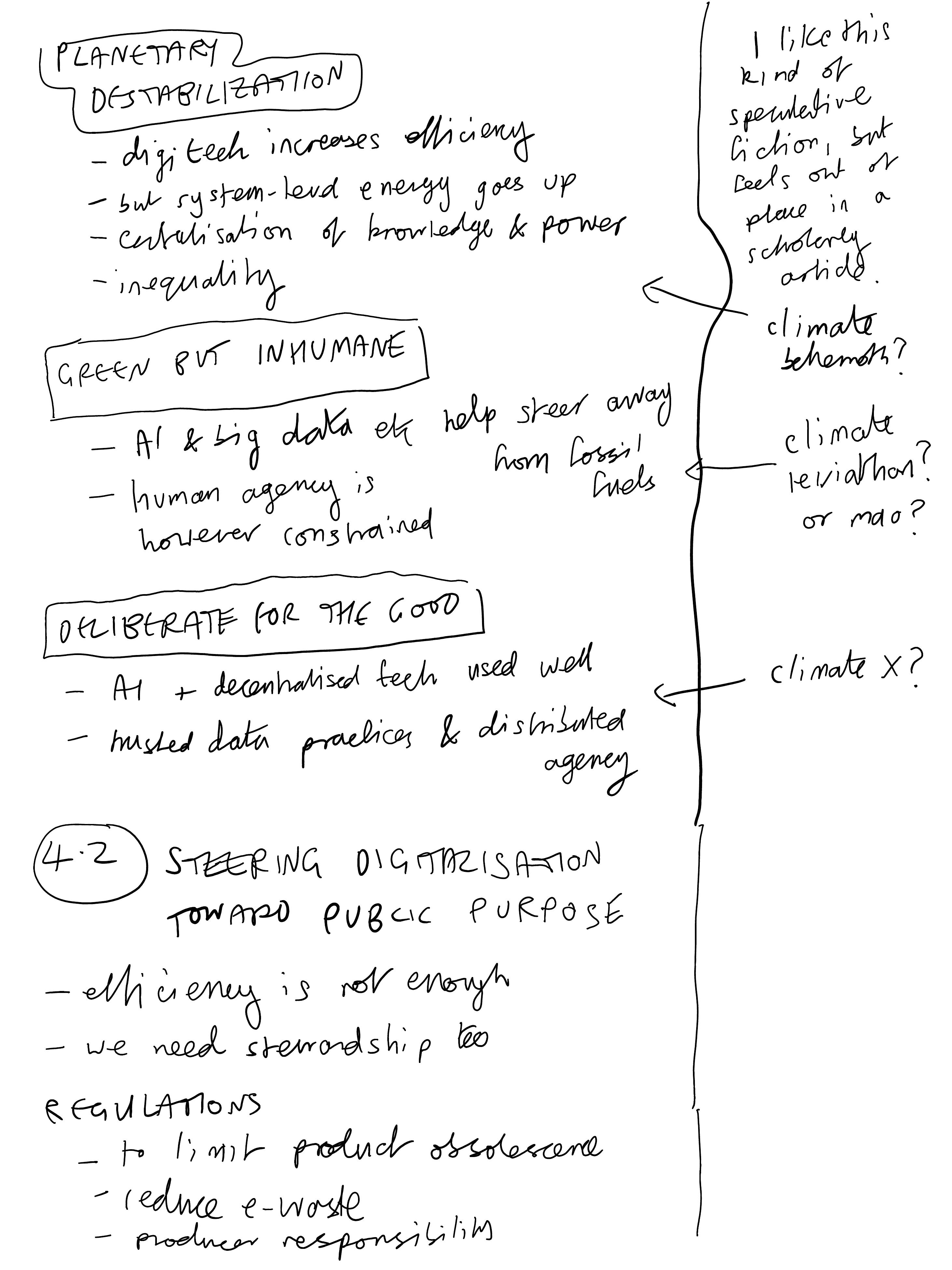

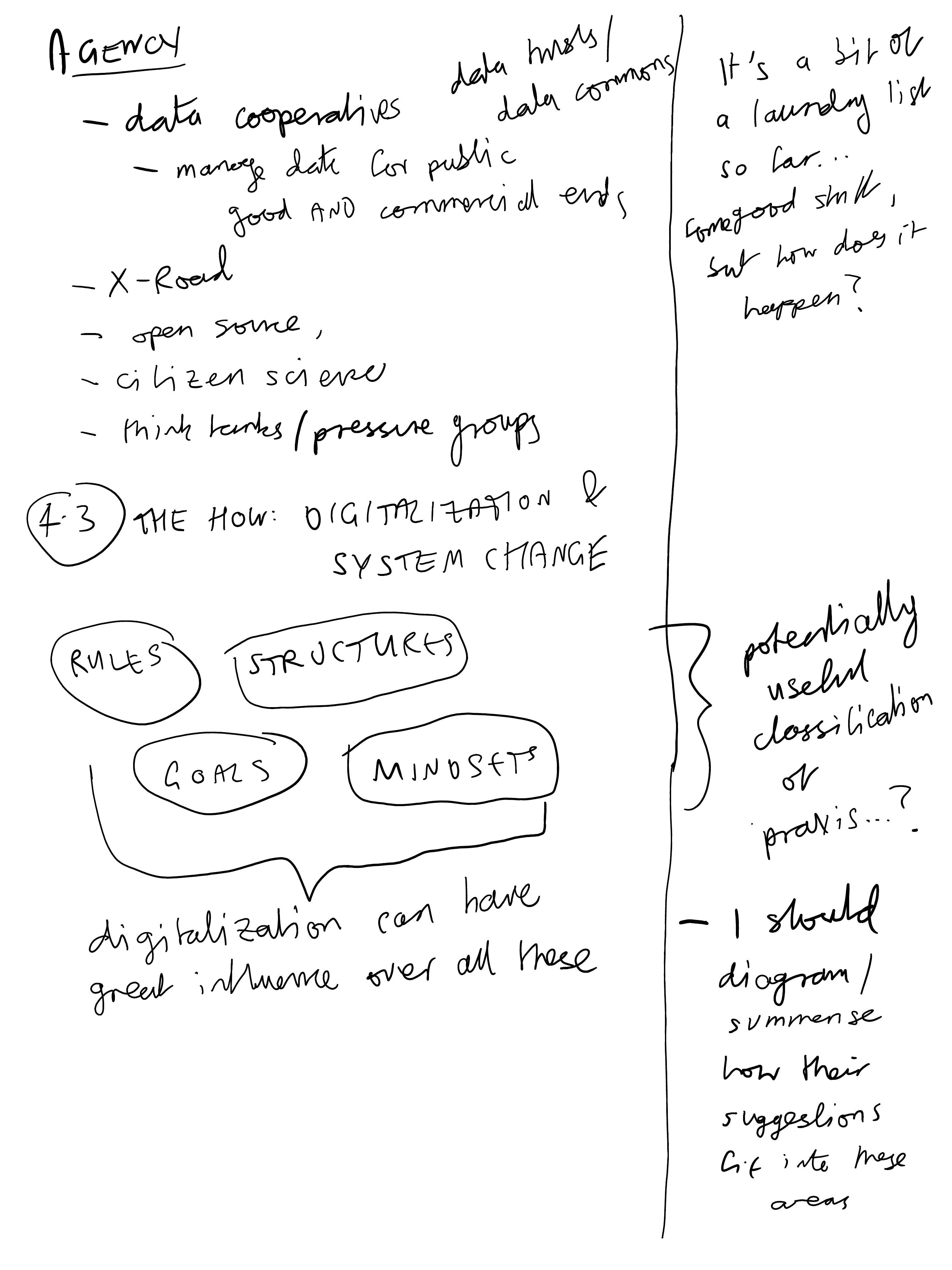
Digitalization has the ability to influence what Meadows highlighted as some of the strongest leverage points over system dynamics: those that alter information flows and controls, rules of the system, the power structures and dynamics that uphold existing rules, and the mindsets that define them.
– page 19
1.1. Leverage points.
1.1.1. Rules and feedback
The first leverage point is the reformalization of rules and feedback, as discussed in the preceding section. Important options include mandatory data sharing in big tech and with urban/local administrations as condition for license; default data management as data commons or data trusts; a requirement for circular electronics designed for increased life span, repair, and reuse; and the use of tax incentives and price signals as feedback to steer digital use cases toward low environ- mental impact.
– page 19
1.1.2. Structures
The second leverage point is the modification of structures and the creation of new ones. Digitalization can play a crucial role by offering a holistic data-based Earth system understanding (116), which would translate into an informational governance that leverages the use of information to drive innovations in governance mechanisms and institutions
– page 20
1.1.3. Goals
The third leverage point is the resetting of goals, at both individual and societal levels, away from aspirational resource-intensive consumption (e.g., private cars, mansions) toward positive outcomes for the commons and society.
– page 20
1.1.4. Mindsets
The fourth and broadest leverage point is a mindset paradigm shift away from disjointed economic, legal, natural, or cultural systems toward a synthetic consideration, as captured by the notion of the Anthropocene
– page 21